Overview
All ASEAN Member States have detailed law and policy frameworks for national disaster preparedness and response. These take different forms, and not all are part of a specific law on disaster risk management. Even where there are such specific laws, their scope and level of detail varies, depending on the objectives of these particular laws within the country’s overall framework for risk management and development.
Types of DRM systems
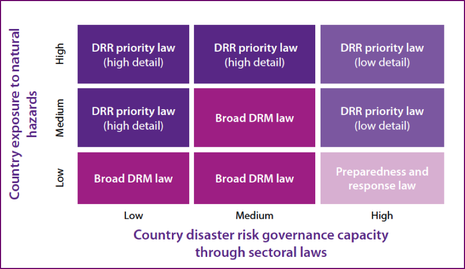
A global method of categorizing national disaster risk management (DRM) laws based on one that was developed by the IFRC and UNDP in the 2014 DRR Multi-Country Law Report.
This matrix indicates where each type of system is generally most useful, suggesting that in the high-risk environment of Southeast Asia most countries would benefit from Broad DRM or DRR priority laws.
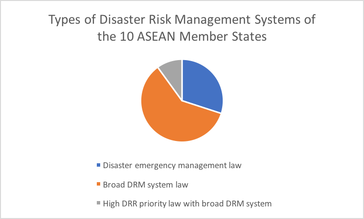
Types of DRM systems of ASEAN Member States
All the ASEAN MS have established permanent DRM systems based on laws and regulations.
- Three are focused more on emergency preparedness and response: Brunei, Malaysia and Singapore.
- The other seven have broad DRM laws (including orders, decrees and regulations), a wide range of risk reduction and mitigation, preparedness and response, and early recovery activities by permanent national disaster risk management institutions: Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Myanmar, Philippines, Thailand and Viet Nam.
- Within this second group, the Philippines’ system has a greater focus on disaster risk reduction.
![]()

