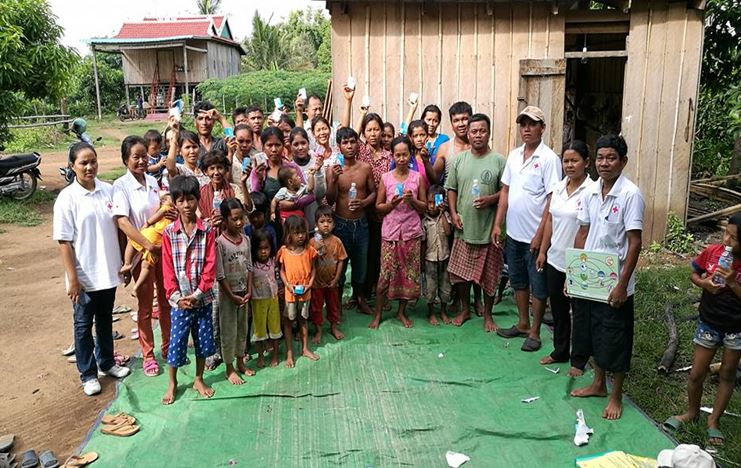
The advanced training course on Emergency Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene (E-WASH) was organized with the support of additional funding from Japanese Red Cross Society (JRCS) and with the purpose of improving the capacity of Lao Red Cross Society (LRCS)’s staff to prepare and respond to disasters in the affected areas. The advance 3-day training course was conducted for 15 WASH focal persons from 5 targeted provinces. The training took place at Luang Prabang Provincial Branch and was participated by 15 Participants, 13 Males and 2 Females, from five provincial RC branches (Oudomxay, Xayabouly, Luang Prabang, Khammouan, and Champasak Provinces).
The training for WASH focal persons included theoretical sessions, table-top exercises, and practical sessions, i.e., installation of the water purification unit and construction of a pour-flush toilet (second day).
LRCs has been receiving funding support from the Japanese Red Cross Society (JRCS) in strengthening E-WASH capacity since March 2016, focusing mainly on Khammouan Province including the procurement and installation of two water purification units (one in Khammouan and one at the National Headquarter in Vientiane).
Two latrines were also installed in a primary school of Baan Sri Boun Heuang which is located in Muang Nam Bak village and about 95 kilometers from Luang Prabang Province. The school consists of two male teachers and a female teacher and 78 students (42 females and 36 males).
Mission report is available here.
Training Presentations:
- Training objective
- General WATSAN in Emergencies
- Introduction to WASH-Related Diseases
- Manpack Installation
- Introduction to Excreta Disposal, Drainage, and Hand Washing Facilities
- Hygiene Promotion
- Assessment, Action Plan, and Monitoring
Video shows students learning about personal hygiene and the 7-step hand washing.
Photos by IFRC Bangkok
![]()


![WASH School-Based Poster [Filipino]](https://www.rcrc-resilience-southeastasia.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/WASH-School-Based-Poster-Final-2.jpg)